[ad_1]
China’s $1tn Belt and Street Initiative infrastructure finance programme has been hit by spiralling dangerous loans, with greater than $78bn-worth of borrowing turning bitter over the previous three years.
The scheme made China the world’s largest bilateral creditor, however the figures counsel it has grow to be a monetary millstone for Beijing and its largest banks.
About $78.5bn of loans from Chinese language establishments to roads, railways, ports, airports and different infrastructure world wide have been renegotiated or written off between 2020 and the top of March this 12 months, in line with figures compiled by New York-based analysis organisation the Rhodium Group.
That is greater than 4 occasions the $17bn in renegotiations and write-offs recorded by Rhodium within the three years from 2017 to the top of 2019.
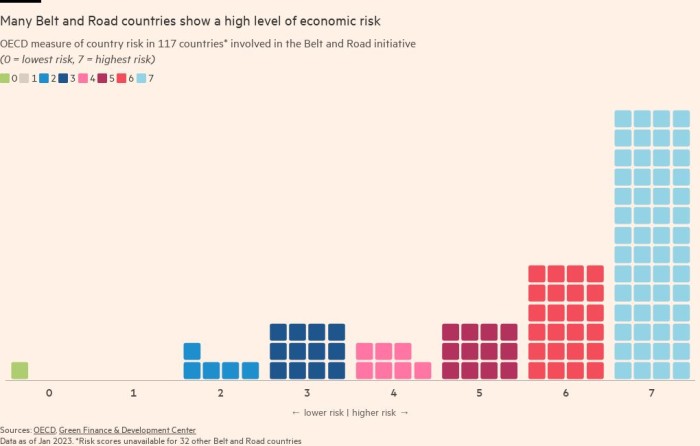
There are not any official figures for the whole scale of BRI lending over the previous decade, however it’s believed to whole “someplace within the ballpark of $1tn”, in line with Brad Parks, govt director of AidData at William and Mary college within the US.
As well as, Beijing has prolonged an unprecedented quantity of “rescue loans” to stop sovereign defaults by large debtors amongst about 150 international locations which have signed as much as the BRI.

The worth of such sovereign bailouts amounted to $104bn between 2019 and the top of 2021, in line with a research by researchers at AidData, the World Financial institution, Harvard Kennedy College and Kiel Institute for the World Economic system. Over an extended timeframe between 2000 and the top of 2021, such bailouts to creating international locations totalled $240bn, the research discovered.
Growing numbers of BRI borrower international locations are being pushed to the brink of insolvency by a slowdown in international progress, rising rates of interest and file excessive debt ranges within the creating world. These international locations’ western collectors, in the meantime, have blamed China for blocking debt restructuring negotiations.
“Frankly, I feel that is solely the start. Chinese language banks have an curiosity in guaranteeing that their largest abroad debtors are sufficiently liquid to proceed servicing their infrastructure challenge money owed,” Parks mentioned. “So, Beijing might be going to be within the emergency lending enterprise so long as its largest debtors are in monetary misery.”
The tempo of BRI renegotiations and write-offs slowed considerably in 2022, in contrast with the height of the pandemic in 2020 and 2021. However consultants mentioned this didn’t point out that the underlying high quality of China’s mortgage guide had improved.
“Removed from it,” mentioned Matthew Mingey, senior analysis analyst at Rhodium. “Whereas some main recipients of China’s lending, like Pakistan, have managed to carry on with IMF and bilateral bailouts, the cracks within the BRI are widening.”
Analysts mentioned they didn’t count on Beijing to name time on the programme that was linked so intently to China’s status on this planet and to the picture of China’s chief Xi Jinping himself. Practically a decade in the past, Xi declared the BRI the “challenge of the century”.
“Many international locations nonetheless welcome investments from China below the framework of the BRI and I don’t see that altering,” mentioned Francesca Ghiretti, analyst at Merics, a Berlin-based think-tank.
Xue Gong, a fellow at Carnegie China, predicted that China would use the Belt and Street Discussion board for Worldwide Cooperation, which Beijing is anticipated to carry later this 12 months, to have a good time a decade of BRI achievements and map out future plans for co-operation.
However she added that Beijing’s overarching concentrate on creating indigenous applied sciences, and a pressure on public funding at dwelling, could lead to fewer sources earmarked for the initiative. “Massive-scale money handouts to state corporations for the BRI are off the desk,” Gong mentioned.
On the identical time, China is broadening its political and diplomatic overtures to the creating world, doubtlessly diluting the significance of BRI over time.
Debt impasse

That is the third a part of a collection on why international locations in financial misery are struggling to maneuver ahead
Since 2021, Xi has launched three strategic initiatives aimed toward remoulding the structure of world governance and diluting the affect of the western-led establishments which have directed world affairs because the finish of the second world conflict.
As Beijing canvasses worldwide assist for 2 of them — the International Improvement Initiative and the International Safety Initiative — these international locations signing as much as grow to be “buddies” of China’s imaginative and prescient are nearly invariably additionally debtors to Chinese language collectors below the BRI.
Cambodia, Mongolia, Cuba, Uruguay, Nicaragua and Belarus have all demonstrated their assist for the GSI throughout current conferences, mentioned Alice Ekman, senior analyst on the European Union Institute for Safety Research. All these international locations are additionally outstanding BRI members.
In the meantime, almost 70 international locations have joined the Group of Mates of the GDI, in line with China’s ministry of international affairs.
[ad_2]